Are you looking for effective ways to secure your Spring applications? Look no further! Our very own Dr. Ing. Max Maass has created a comprehensive 3-part series on Spring Actuator Security, covering everything from identifying vulnerabilities to implementing best practices. On today's episode we will discuss how we can detect exposed Spring Actuators in an application that you have source code access to. We will begin with manual steps, and then look at how you can automate the process using static security testing tools (dynamic testing will be covered in part 3 of the series).
In the first part of this series, we have discussed the risks inherent in exposing the Actuator functionality of the Spring framework. If you haven't read that part yet, I recommend that you do so before reading this article.
Part 2: Finding Actuators using Static Code Analysis with semgrep
- Manually Looking for Exposed Actuators
- Automating the Search using Semgrep
- The Basic Case: All Actuators
3.1 Matching Specific Actuators
3.2 Excluding Findings - Conclusion
1. Manually Looking for Exposed Actuators
The most basic method of finding dangerous actuators is to use... your eyeballs. If you have access to the application source code, you can look at the Spring configuration files to check if actuators are enabled, and how they are configured. Begin by checking the .properties file(s) (or the respective .yaml equivalents) where the Spring configuration is stored. Recall that the list of active actuators is controlled with the following key:

This setting controls which endpoints are exposed over the web. Individual endpoints can also be completely disabled by setting management.endpoints.$ACTUATOR.enabled=false - as a rule of thumb, I would recommend inspecting everything in the management category and see if any dangerous endpoints are being activated, and if so, if mitigations (authentication requirements, ...) are already in place.
(All examples in this article are targeting the current version of Spring - older versions may use a different configuration syntax, or even (in the case of Spring 1.X) expose all actuators by default. Adapt what you read to your version of Spring, if necessary.)
2. Automating the Search Using Semgrep
Checking the code manually isn't always feasible. Maybe you are part of a security team that is responsible for a large set of software repositories, or maybe you want to add a check for dangerous actuators to your CI, to ensure that they aren't inadvertently activated a few weeks down the line.
For these cases, let me introduce you to my favourite static code analysis tool: semgrep. It's a free Open Source tool that you can install and use right now (it only starts costing money if you want to use their dashboard to view the results, which is entirely optional, and all code scanning runs on your device - code is never uploaded to any servers). Stated briefly, semgrep searches for code matching specific patterns, taking the semantics of the code into account (hence, semantic grep). You can use it for security checks based on a large set of detection rules curated by the semgrep community, but where it really shines is when you start writing rules for your own use cases.
3. The Basic Case: All Actuators
Semgrep rules are fairly easy to wrap your head around, so let's build one for our example application from the previous part of this series. To be able to showcase some of the capabilities of semgrep, we'll be using the YAML configuration syntax for Spring. This is what a basic vulnerable Spring configuration could look like:
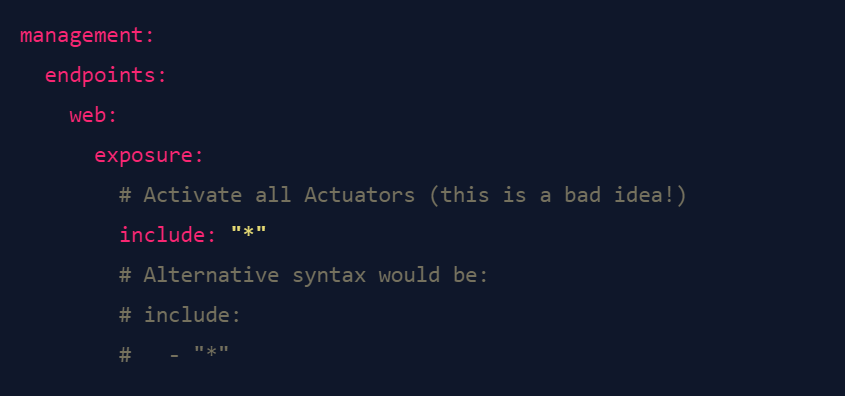
Semgrep patterns are also specified in YAML files. Here's an annotated semgrep rule to find this case, with explanations what the components are doing.
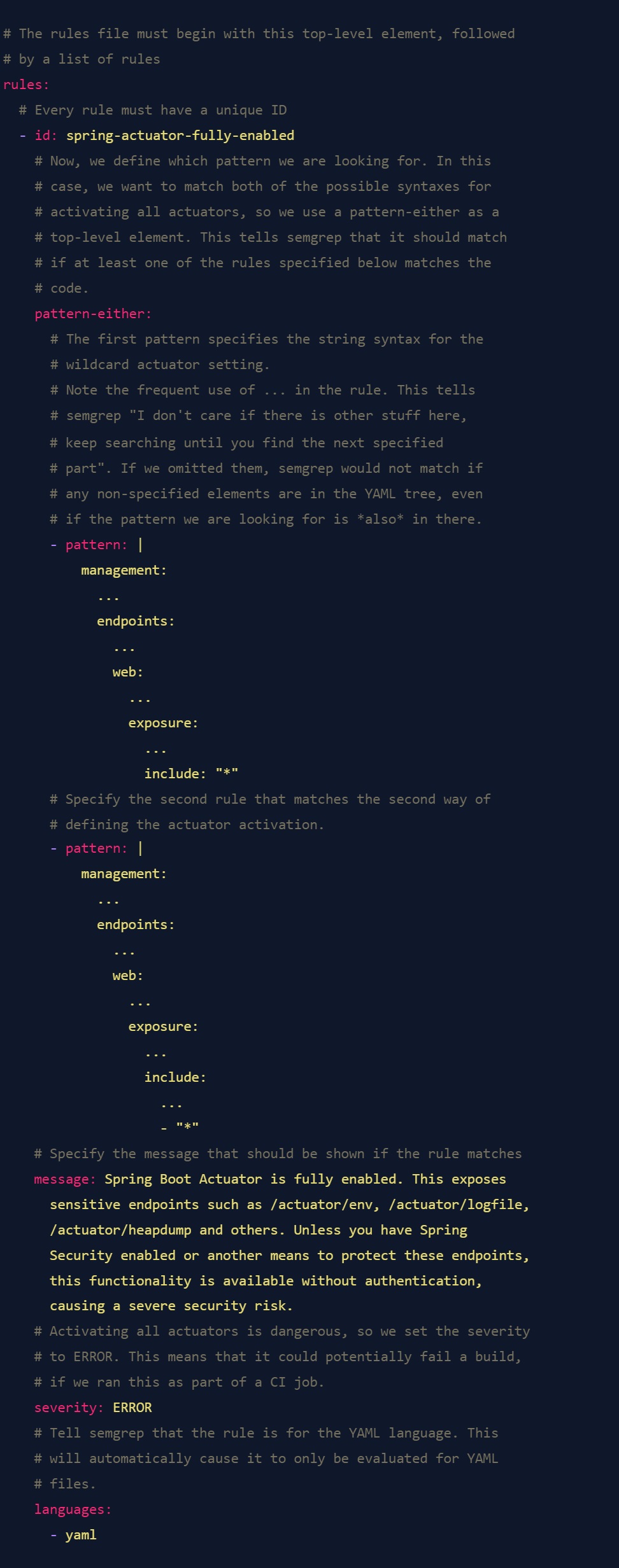
This is already quite a handy rule to quickly audit a large codebase for an obvious misconfiguration. To run it, save it in a file, and then run it with semgrep like this:
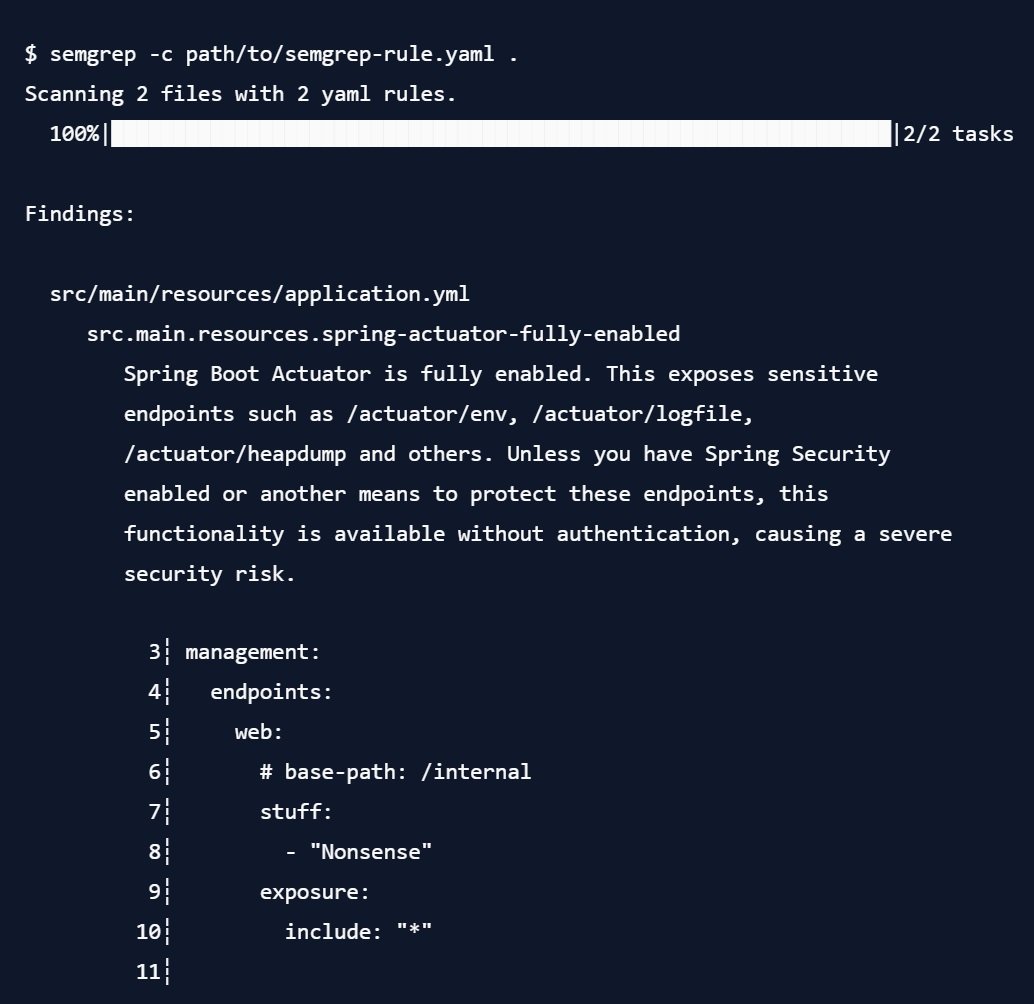
Note that it outputs the entire matched area of the code for inspection. It also did not have any problems with the commented-out section, or with the other YAML keys I added to the config file. Pretty neat, and something that would be difficult to achieve with a regular grep call.
3.1. Matching Specific Actuators
The example above is already quite handy, but it only checks for the wildcard operator. Where semgrep really starts to shine is if we encounter a configuration like this:
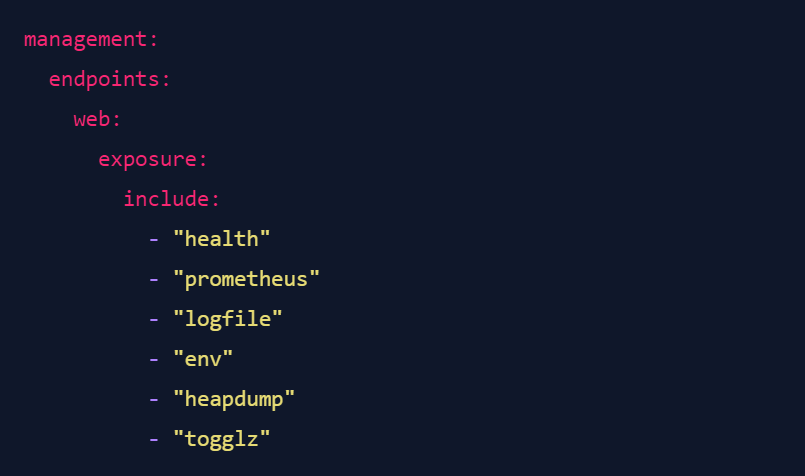
Now, for the sake of argument, let's say you are fine with exposing your health endpoint (which can be reasonable in some situations), and you also find it acceptable to expose the Prometheus metrics (I wouldn't recommend it, but you do you). All other actuators should be disabled. But how can we check this using semgrep?
Fairly easily, it turns out. Semgrep has a powerful feature called "Metavariables", which allows you to pull specific parts of the code into a variable that you can then reuse in other parts of the rule. Normally, this would be used to track variables or function names while analyzing source code. However, we can also use it to pull out the list of activated actuators and match them against a list of known-accepted actuators. Here's an annotated rule that does this:
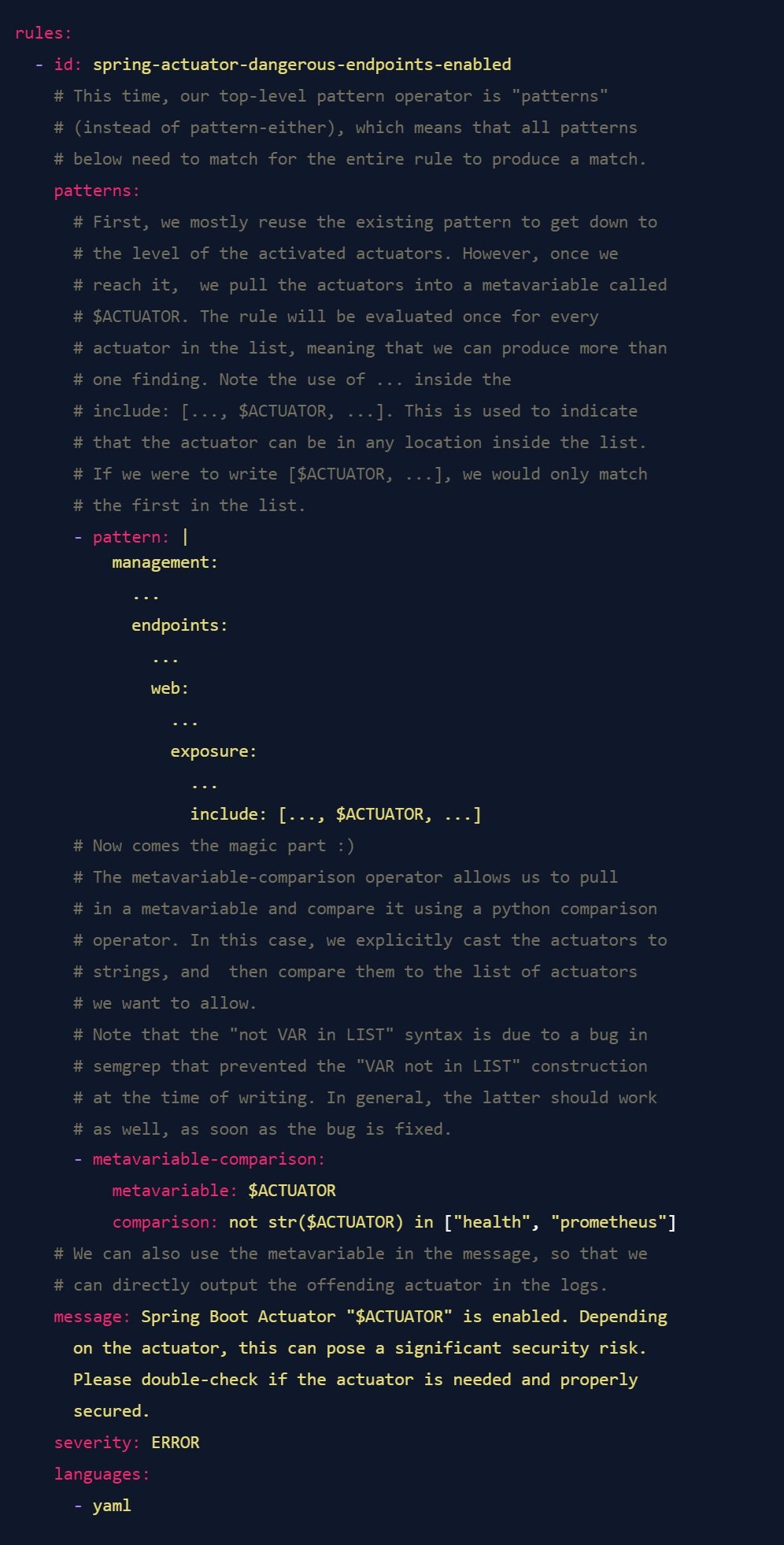
If we run this rule against the configuration shown above, we get the following result:

You will note three things:
- The output of the metavariable is a bit bugged - this is a known issue in semgrepat the time of writing, but it is purely cosmetic (internally, the matching works).
- We get four matches, which is the expected number for the configuration file above - health and prometheus were ignored, as requested.
- Although we defined the rule using the syntax
include: [..., $ACTUATOR, ...], it still matched the syntax from the config file, as it knows that the inline list format and the "individual lines prefixed by a dash"-Syntax are equivalent. This semantic knowledge is what makes semgrep so powerful.
3.2. Exlcuding Findings
This is already a quite useful pattern. However, maybe your organization actually wants actuators to be active, and simply requires them to be running on a specific port or IP that is not exposed publicly. In that case, a configuration like this would be perfectly acceptable:
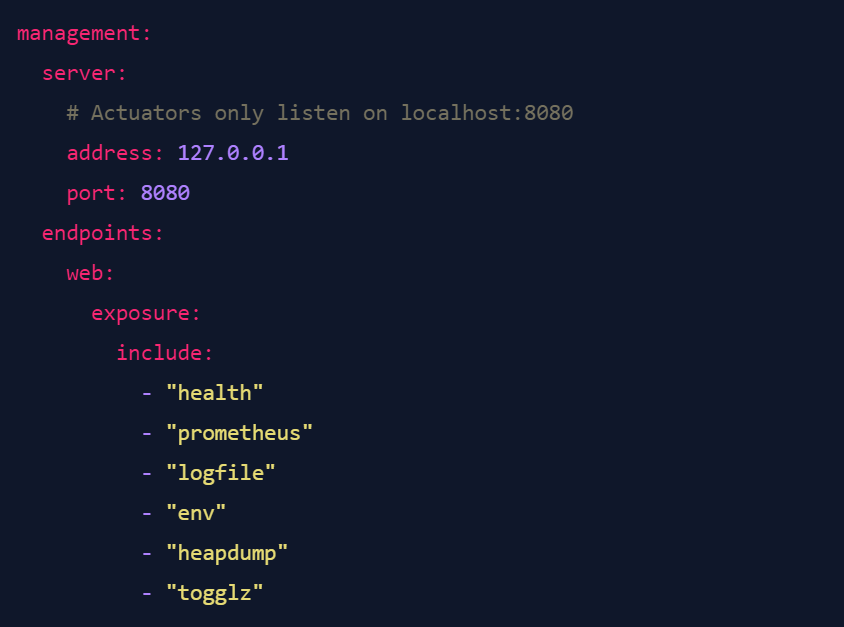
So, how can we tell semgrep "please find cases where actuators are active, but not if they are only listening on a specific IP"? Fairly easily, actually. Let's build a rule for that.
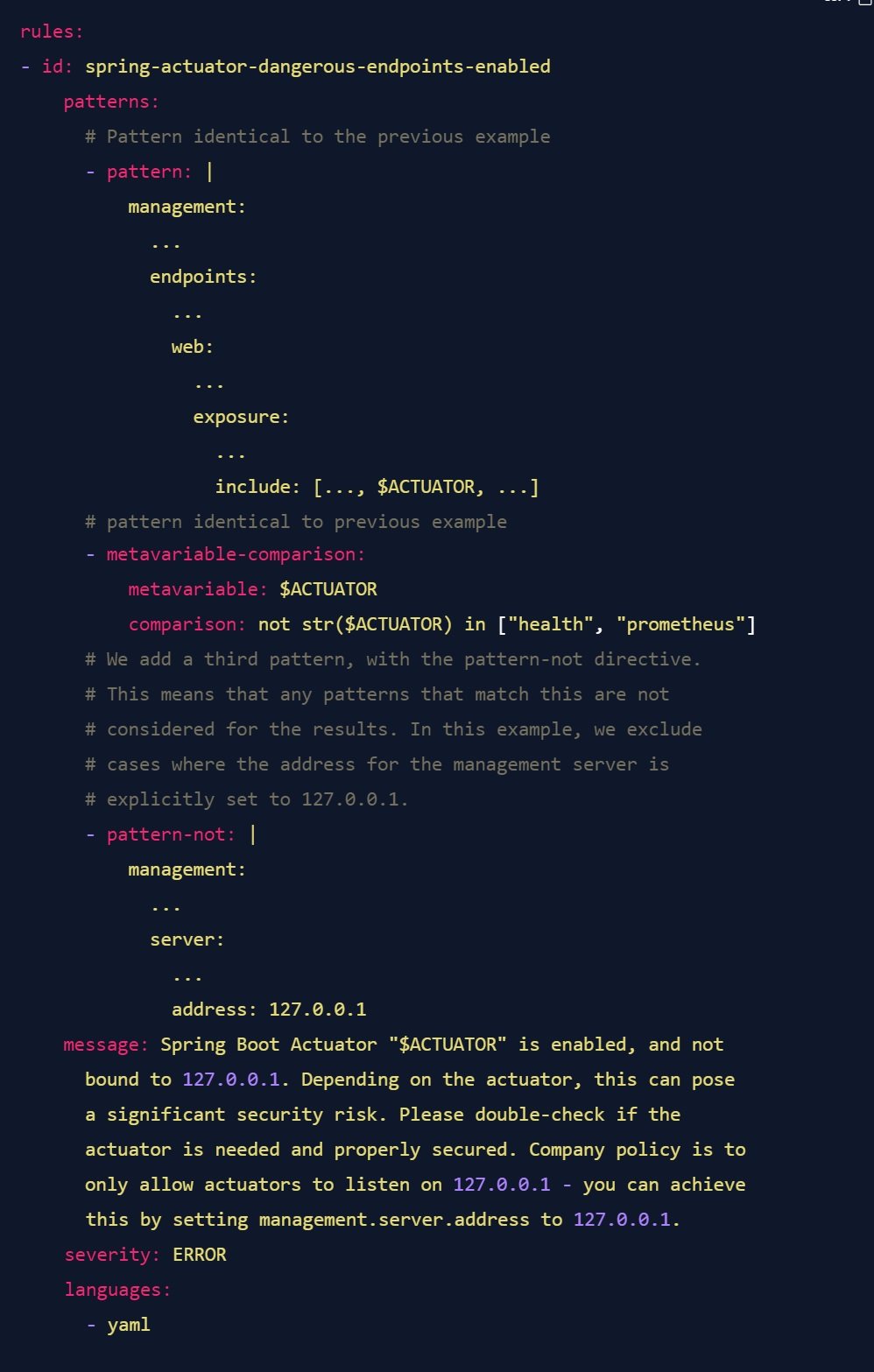
Or maybe you don't actually care which IP the actuator is listening on, as long as a port and IP are explicitly set - maybe because the set of possible allowed IPs is too large, or maybe because you think that if a team is going to go to the trouble of setting these two values, they know what they are doing and don't need your handholding. In this case, simply change the pattern-not to the following:
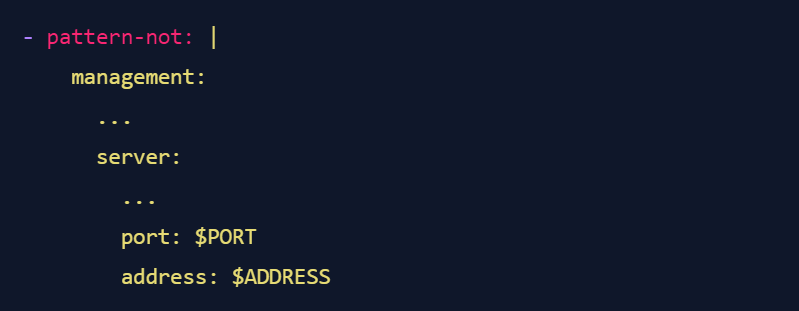
In this case, you simply tell semgrep "hey, I don't actually care what the values of the two metavariable are, just make sure they are present". As a bonus, semgrep knows that the order of keys in YAML doesn't matter, so you don't have to worry about what happens if the two keys are in a different order in the config file - semgrep will find them.
4. Conclusion
We could go on for quite a while in refining these patterns, but in the end, you will have to adapt them to your own situation. For example, maybe you are securing your Actuators using Spring Security, and simply need to check if the correct authentication requirements are configured. Or maybe you are exposing all active actuators, but have turned off most actuators that are enabled by default. All of these things can be checked with semgrep, if you know how to write the rules.
I would be remiss if I did not mention one limitation of semgrep: Currently, the semantic features of semgrep are not yet available for all programming languages. In particular, this is the reason why I worked with YAML configuration files for Spring in this article - going through the plain-text properties format would be a lot more annoying with semgrep, as you cannot use the implicit hierarchy that YAML gives you to structure your queries. You can still write semgrep rules against these files using the generic language model, but it is subject to some limitations. I recommend playing around with it to see if you can get your use case to work - the semgrep playground allows you to do so without installing anything on your device.
I have contributed the rules from this article (written in a slightly nicer way that would have taken a bit longer to explain, so I opted to go with simpler rules for this article) to the semgrep rule registry, including a rule that uses the generic mode to find Actuator activations in .properties files. You can find the final rules in this pull request on GitHub.
And as a bonus: If you want to scan a large set of Git repositories with a set of semgrep rules, I wrote about how you can do this using the OWASP secureCodeBox, an Open Source project that I am an active contributor to.
This concludes this part of the Spring Actuator security series. I hope that you have gained some appreciation for the power and flexibility of using static code analysis to aid you in securing your systems. In the next part, we will discuss how to find actuators in deployed software using dynamic testing.
Further Reading:
- The semgrep documentation and Getting Started tutorial
- The semgrep registry contains lots of rules for many issues, and you can contribute your own.
- The semgrep Slack is full of helpful and kind people who help you when you are stuck.
Once again, I would like to thank the Security Community at my employer, iteratec, for their input on this issue and feedback on the article. Additionally, I would like to thank the Semgrep community on Slack for their help in learning how to write rules - you rock!
Dieser Blogbeitrag erschien ursprünglich auf: https://blog.maass.xyz/spring-actuator-security-part-2-finding-actuators-using-static-code-analysis-with-semgrep
Mehr Infos und weitere interessante Beiträge unter: https://blog.maass.xyz
Blog abonnieren
Weitere Artikel
- Februar 2026
- Januar 2026
- Dezember 2025
- November 2025
- Oktober 2025
- August 2025
- Juli 2025
- Juni 2025
- Mai 2025
- April 2025
- März 2025
- Februar 2025
- Januar 2025
- Oktober 2024
- September 2024
- August 2024
- Juli 2024
- Juni 2024
- Mai 2024
- April 2024
- März 2024
- Februar 2024
- Januar 2024
- Dezember 2023
- November 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- Juli 2023
- Juni 2023
- Mai 2023
- April 2023
- Februar 2023
- Dezember 2022
- November 2022
- Mai 2022
- April 2022
- März 2022
- Januar 2022
- Dezember 2021
- November 2021
- Oktober 2021
- August 2021
- Juli 2021
- Juni 2021
- Mai 2021
- April 2021
- Dezember 2020
- Oktober 2020
- September 2020
iteratec
iteratec ist der Partner für alle, die zu den Gewinner:innen der digitalen Transformation gehören wollen. Mit individuellen, überlegenen Lösungen eröffnen wir unseren Kunden technologische wie unternehmerische Potenziale. Denn: Wenn Scheitern keine Option ist, sind wir der Partner, der den Unterschied macht. So haben wir seit 1996 mehr als 1.000 Projekte zum Erfolg geführt und eine Kundenzufriedenheit von 97%.